EPANET-BAM
EPANET-BAM 1.0 is an augmented version of EPANET 2.00.10, open-source software distributed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency that models flow and contaminant transport through water distribution pipe networks.
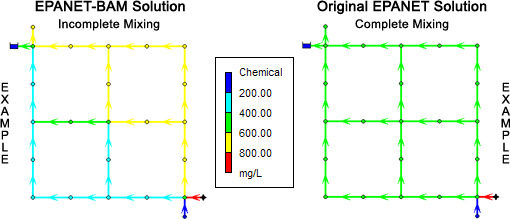
EPANET-BAM uses a new Bulk Advective Mixing (BAM) model to predict concentrations of an aqueous solute at the outlets of cross junctions in a water quality simulation.
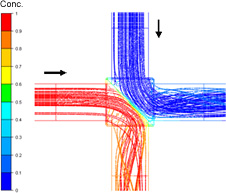
Recent experimental and computational studies have shown that solute mixing in pipe junctions is incomplete, contrary to the assumptions of the complete-mixing model used in the original EPANET. These studies found that fluid streams entering the junction tended to bifurcate, depending on the relative momentum of the fluid streams, which resulted in incomplete mixing. Click here to see more details of the computational fluid dynamics modeling.
The Bulk Advective Mixing (BAM) model honors this observed behavior by retaining bulk fluid momentum. It also neglects turbulent diffusivities and instabilities at the impinging interface. Therefore, Bulk Advective Mixing is a lower bound to the amount of mixing that can occur in a junction, whereas complete-mixing is an upper bound.
EPANET-BAM uses a mixing parameter to scale between the predictions of the complete-mixing and BAM model predictions.
Source: Sandia Corporation
Leave a Reply